What is Apache Wayang™?
A unifying data processing framework that seamlessly integrates and orchestrates multiple data processing systems to deliver performance and flexibility.
Apache Wayang's three-layer architecture provides a strategic abstraction between user applications and underlying data processing platforms, ensuring seamless integration among heterogeneous systems. The application layer encapsulates application-specific logic, while the core layer acts as an intermediary, translating application logic into an intermediate representation (Wayang plan). The Wayang plan is then transformed into an execution plan in the platform layer, where each operator is assigned to be run on a specific platform selected from a diverse pool of execution engines, including but not limited to any database, Apache Spark, Apache Flink, and ML systems. This abstraction allows for cross-platform optimization and execution.
One of Wayang’s key innovations is its cross-platform optimizer, which automates data system selection and spares users from making complex platform choices. This optimization process ensures that the resulted execution plan is tailored to the specific strengths and capabilities of each data engine, maximizing performance and efficiency.
Apache Wayang's core strength lies in its cross-platform task execution, enabling developers to seamlessly combine the strengths of various processing engines, such as Spark, Flink, and Tensorflow, in one pipeline. Designed with flexibility as a priority, Apache Wayang enables easy extensibility to accommodate new operators and data systems. The platform's extensibility and ease of use makes it a compelling choice for data engineers and developers seeking a unifying and versatile data processing solution.
Architecture and Software stack
Apache Wayang's unique architecture, unlike traditional DBMSs, decouples the physical planning and execution layers, empowering developers to express their data processing logic in a platform-agnostic fashion. This separation of concerns allows developers to focus on the algorithmic aspects of their applications without being constrained by the intricacies of specific processing platforms.
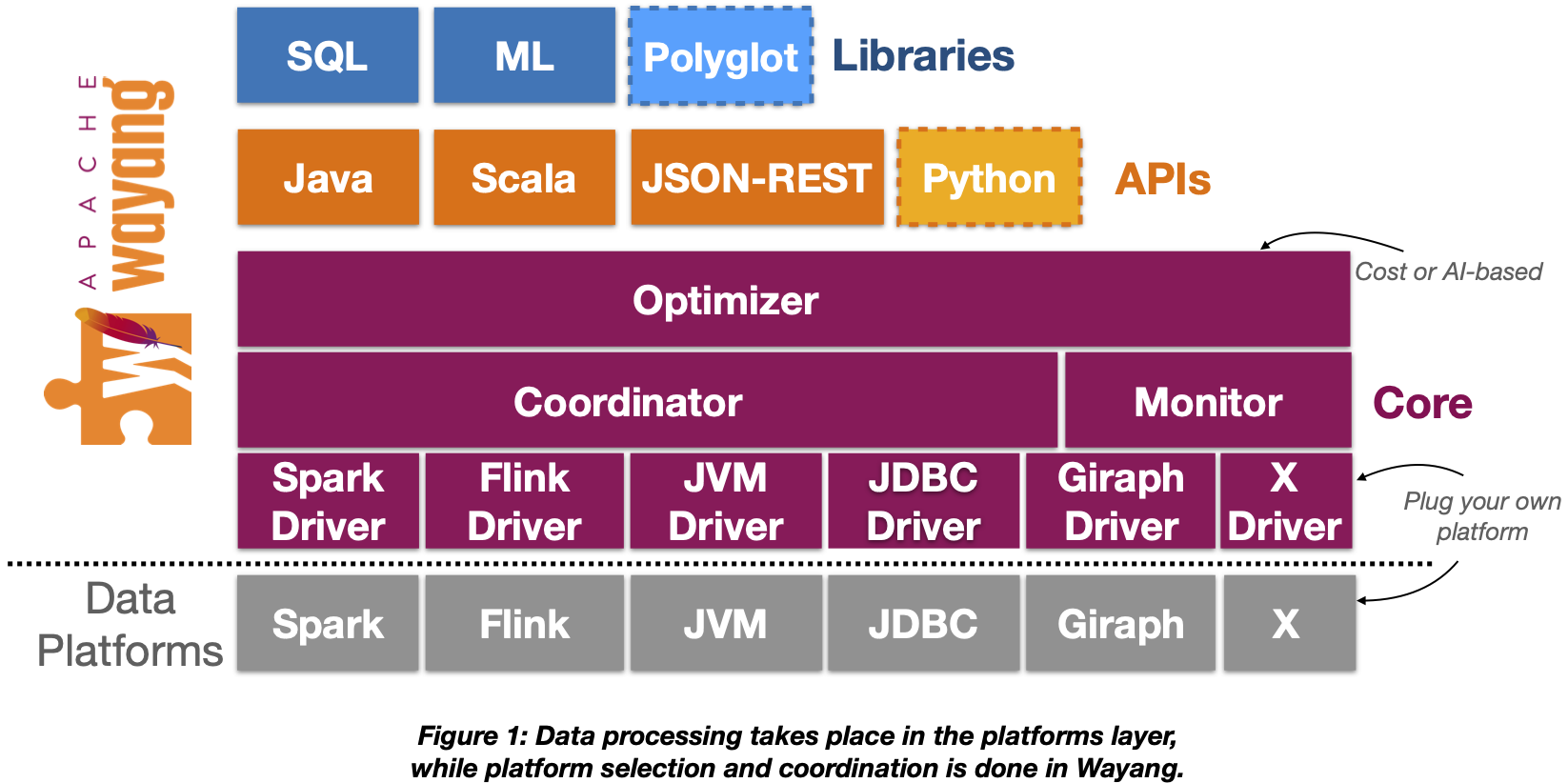
At the bottom layers of the software stack, there are the different data storage mediums and the supported data processing platforms. On top of these, Wayang’s core consists of the following main components: the optimizer, the executor, the monitor, and platform-specific drivers. Wayang currently supports two main APIs: the Java one and the Scala one. A Python API is also supported with limited operator coverage for the moment. Besides using any of the supported languages, users can directly input SQL queries via the SQL library, which transforms them into a Wayang plan. Wayang also comes with an ML library for running ML tasks. Users can directly utilize the provided algorithms or can implement their own algorithm using a simple ML abstraction. To enable support for more programming languages in an efficient way, Wayang will soon come with a Polyglot library.
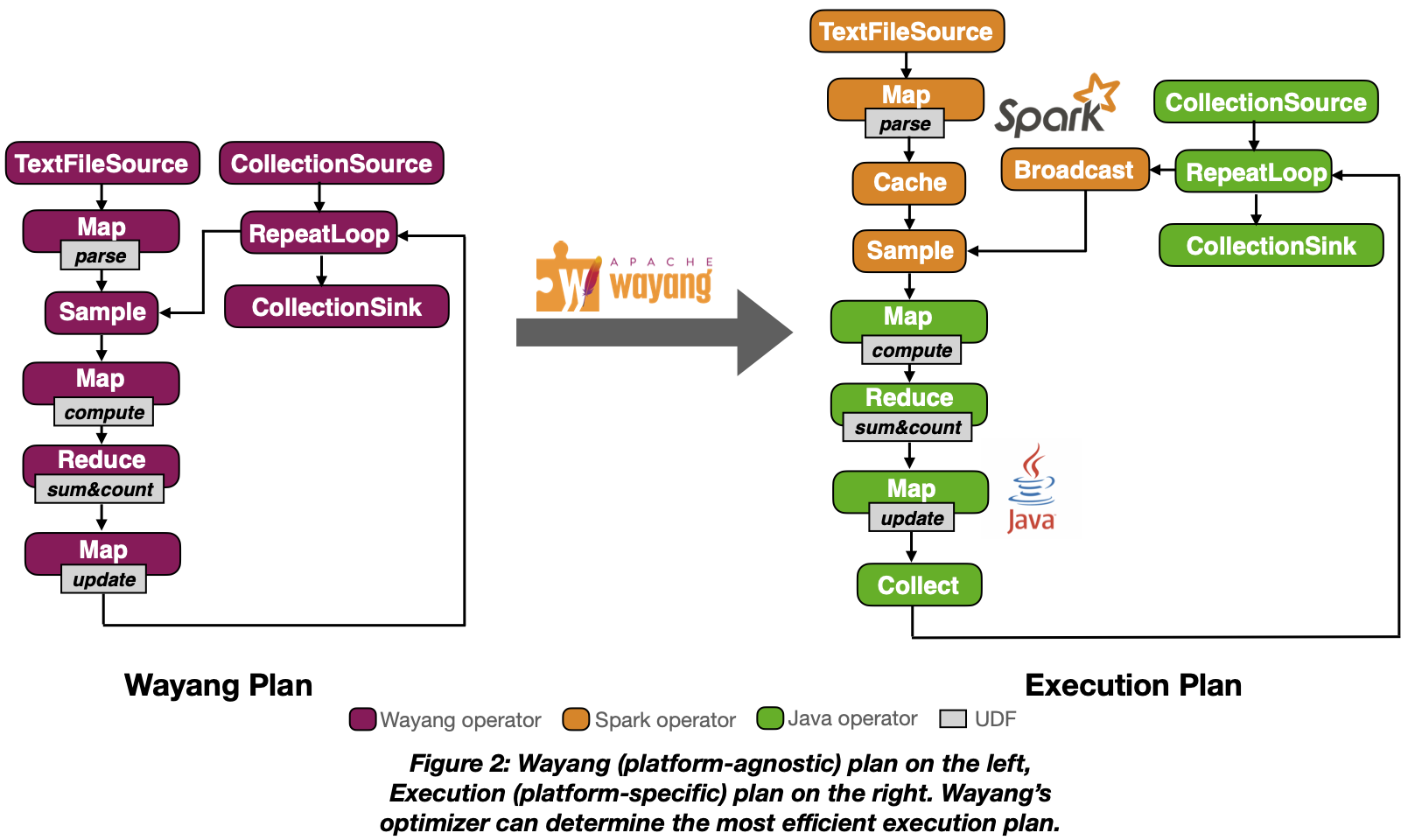
Below you can see on the left, a Wayang plan representing the stochastic gradient descent algorithm, which used in most deep learning tasks. On the right, you can see how the optimizer decided to execute it. Orange nodes are the operators that ran on Spark and green the operators executed as a single Java process.
Query Optimizer
Wayang's query optimizer is the principal component of the core. It receives as input a Wayang plan and outputs an execution (platform-specific) plan (see example plan above) with the goal of minimizing the total cost. The metric for the cost can be anything, from execution runtime to monetary cost or energy consumption. To achieve this, the optimizer first “inflates” the plan: For each node that corresponds to a Wayang operator, it adds all the corresponding execution (platform-specific) operators. Once the inflated plan is created, the optimizer attaches not only the operator’s costs but also the costs for moving intermediate data from one platform to another. By default, Wayang uses linear cost formulas to estimate these costs but one can plug their own optimizer, e.g., an ML-based one. At the last step of query optimization, our enumeration algorithm considers available options to output the optimal execution plan w.r.t. a defined cost.
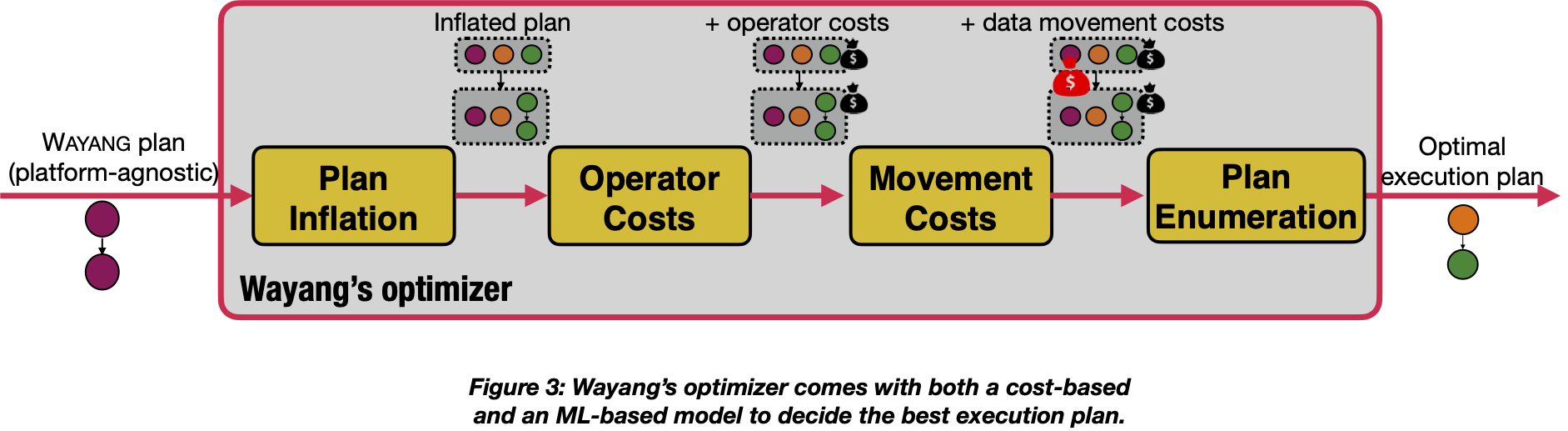
Note that users can control the optimizer by specifying in their code where an operator has to be executed via the withTargetPlatform(plat) call on the desired operator. Then, the optimizer takes into consideration the decisions of the user and outputs an execution plan by navigating a reduced search space during the plan enumeration.
History
Wayang (formely called Rheem) is the product of many years of top quality research. Below you can find the main publications:
-
Apache Wayang: A Unified Data Analytics Framework. SIGMOD Rec. 52(3): 30-35 (2023) pdf
-
Apache Wayang in Action: Enabling Data Systems Integration via a Unified Data Analytics Framework. SIGMOD Conference Companion 2025: 35-38 pdf
-
ML-based Cross-Platform Query Optimization. ICDE 2020: 1489-1500 pdf
-
RHEEMix in the data jungle: a cost-based optimizer for cross-platform systems. VLDB J. 29(6): 1287-1310 (2020) pdf
-
RHEEM: Enabling Cross-Platform Data Processing - May The Big Data Be With You! -. Proc. VLDB Endow. 11(11): 1414-1427 (2018) pdf